Obesity is a dense accumulation of fat in the body that poses a health risk where the body fat measure (body mass index) based on height and weight has a value of 30 or higher. Obesity, which also affects diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, liver disease and sleep apnea, is a curable disease. Physical activity, healthy eating and behavioral changes are used in the treatment of obesity by helping to lose weight. In some cases, drug treatment or surgical methods developed against obesity can be used.
What is Obesity?
Obesity is a condition in which the ratio of a person’s height to weight in kilograms, i.e. the body mass index, is above 30 as a result of consuming more calories than the body can use. It is a condition in which the body mass index (BMI) is not suitable for height and body structure. Obesity is also known as fat in the abdomen and internal organs. An unbalanced increase in body fat can lead to cardiovascular diseases and consequently to vascular occlusion, stroke and cholesterol. Obesity or being overweight also brings shortness of breath.
Obesity is a rapidly progressing disease in the world and in our country. Obesity rates are increasing day by day. Obesity is a disease that reduces the quality of life as the average life expectancy increases, reduces the production capacity of people and must be treated.
What are the Symptoms of Obesity?
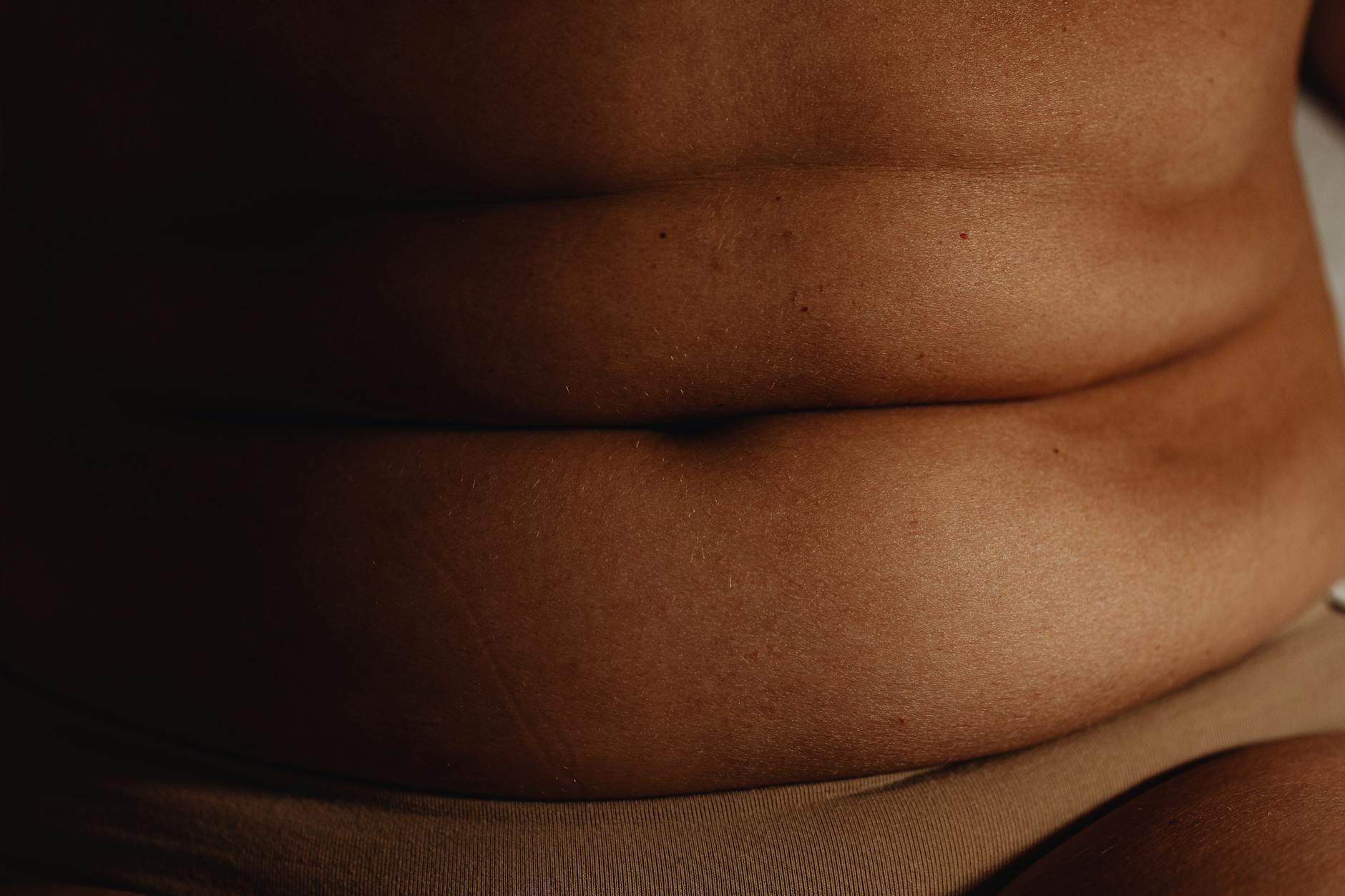
The first and most obvious symptom of obesity is the increase in the rate of body fat. The symptoms seen with the development of obesity are listed as follows:
- Fat accumulation around the waist
- Sleep apnea, snoring and difficulty sleeping
- Constant and excessive sweating
- Shortness of breath
- Difficulty with physical activity
- Feeling weak and tired all the time
- Skin problems such as rashes, acne and infections
- Joint and back pain
- Leg pain due to excess weight
- Psychological problems such as depression and social isolation
- Intolerance to heat
What Causes Obesity?
Obesity can be caused by psychological problems or hormonal factors. However, the biggest factor in the development of this disease is sedentary life and unhealthy diet.
It is possible to list all the reasons that cause obesity as follows:
- Excessive and wrong eating habits
- Inadequate physical activity
- Age, gender, education level, socio-cultural factors, income status
- Hormonal and metabolic factors
- Genetic, psychological factors
- Frequent very low energy diets
- Smoking and alcohol use habits
- Some medications used (antidepressants, etc.)
- Number of births and frequent birth interval
- Inadequate breast milk intake
- Excessive and wrong eating habits
Consuming fatty foods, eating fast-food foods and making this a habit increases the body’s fat content and paves the way for obesity.
Lack of physical activity
Inactivity or not exercising regularly, supported by an unhealthy diet, causes the body not to burn fat, leading to obesity.
Age, gender, education level, socio-cultural factors, income status
A person’s level of education, region of residence, surrounding culture, income status and gender can lead to obesity by bringing along various problems.
Hormonal and metabolic factors
Due to hormonal imbalance in the body and slow metabolism, the body has difficulty in burning fat and causes the person to gain excess weight. Medications used due to hormonal imbalances can cause obesity by stimulating appetite.
Genetic, psychological factors
Depression, anxiety and mood disorders, especially depression, are the main factors in the emergence of obesity. Especially social environment and family relationships can also cause obesity. A family history of obesity is also a risk factor.
Applying very low energy diets at frequent intervals
Continuous low-calorie diets can cause a decrease in metabolic rate with the effect of age. In cases where there is little movement, weight gain occurs and causes obesity.
Smoking and alcohol use habits
The incidence of obesity is known to be 1.2 times higher in smokers. Smokers have the potential to eat more and gain weight. With increased weight gain, they may develop obesity.
Some medications used (antidepressants etc.)
Some medications used against chronic diseases can cause a person to gain weight by increasing appetite. Antidepressants, especially those used against psychological problems, can cause weight gain if not taken carefully.
Number of births and frequent birth interval
It is seen that the increase in the number of births and the decrease in the birth interval lead to weight gain in women and pave the way for obesity.
Inadequate breast milk intake
A weak immune system due to insufficient breast milk intake and poor development of metabolic and hormonal processes can lead to obesity.
